Solar PV example: single garage
This is an example design of a UK solar PV system.
- Location: Cambridge 52.2degN, 0.14degE
- Detached single garage
- Flat roof 3x5m
- Orientation: east-west
- Prevailing wind: westerly
This is quite a small roof area and the flat roof means we have to build our own structures, we cannot rely on the roof pitch to incline our panels.
According to Global Solar Atlas, 1 kilowatt-peak (kWp) pointed due south at 38 degrees of inclination returns 983kWh per year. This model includes compensation for cloud cover and panel efficiency at site temperatures. It assumes a full view of the sky.
Let's design for our site.
Due to the roof having the long edge going east-west, we could mount four panels on frames angled due south, with one short edge meeting the long edge of the roof, and the other short edge of the panel about 1.2m in the air. This is not ideal as it will be subject to strong crosswinds and need substantial anchoring to avoid the panels acting as a sail. It is also aesthetically less pleasing and may be awkward from a planning permission perspective.
Instead it makes more sense to align the panels east-west rather than due south. This is because we can butt a pair of panels, one facing east and one facing west, and have two pairs of panels on the roof. Each panel is about 2m x 1m and about 400 watt-peak. Using an east-west alignment also gives a smoother generation profile across the day, and also a better wind profile.
A simple mounting solution for flat roofs is the Renusol Console bucket system: you just put the plastic tub on the roof, fill it with ballast, and screw the panel to it. No attachment of the bucket to the roof is required. These mount the panels at 15 degrees inclination.
Let's do the calculation for 15 degrees and two panels of 400Wp each, facing east. GSA link. For 1kWp (GSA won't go lower) we'll generate 808kWh, so scaling down to 800Wp it'll generate 646kWh.
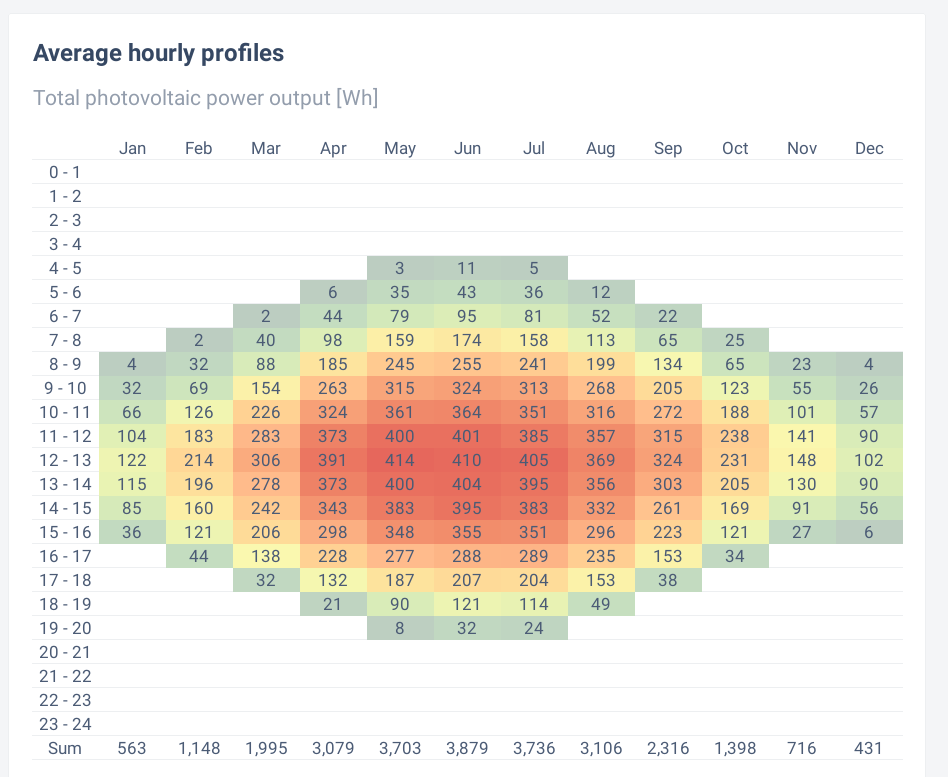
For the west facing panels, GSA gives 795kWh for 1kWp, so that's 636kWh for 800Wp.
Therefore our system is predicted to generate 646+636=1282kWh per year.
The cost of that electricity will vary based on tariff, but if entirely replacing grid electricity at 35p/kWh it would save £448.70 per annum. If it was fed back to the grid at a Smart Export Guarantee rate of 4p/kWh it would earn £51.28pa, and at an Octopus Agile Outgoing average rate of 34p/kWh (source MSE 20-09-2022) it would earn £435.88.
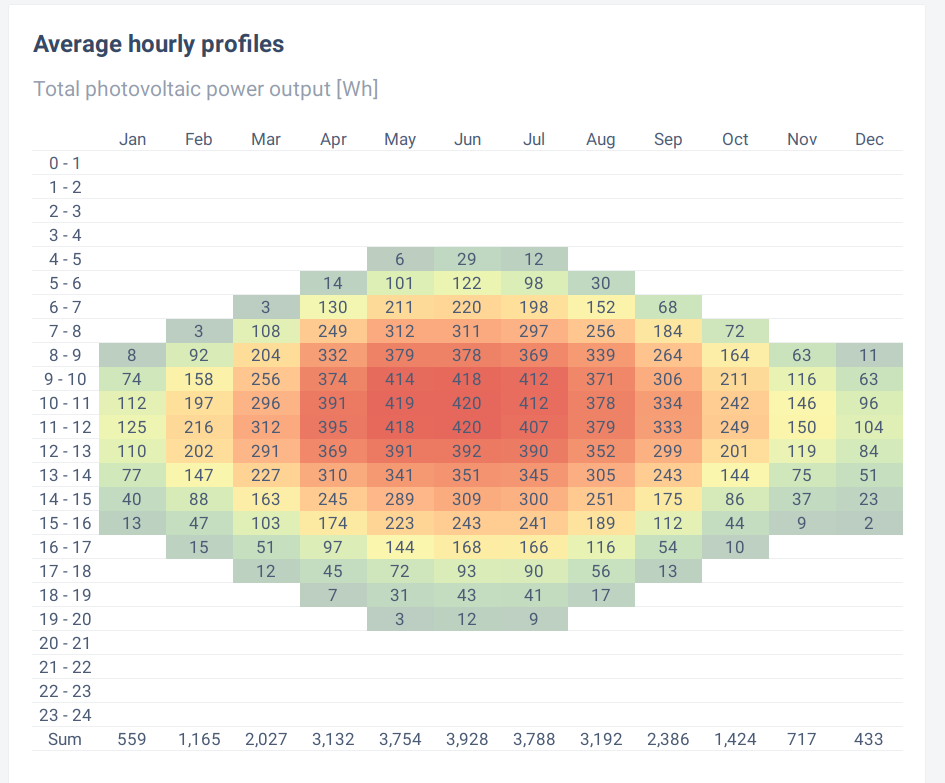
These figures give plots of generation for the east and west facing panels at different times of the day in different months. Obviously there is more generation in the summer months, not least due to longer days. However there is still meaningful generation in February and October (about 2kWh per day).
Generation profile for 1kWp panels facing due east: